簡介:智能井完井技術中,動態控制很重要。其四大作用包括提高最終采收率、增進/優化產能��,減少井下作業量和環境影響最小化����。
INTELLIGENT WELL COMPLETIONS
Active control is a key factor in intelligent well completions
Maximize final recovery of reserves through an exploitation strategy based on maximum control, real-time monitoring and closed-loop capability.
Jesus Contreras and Fernando Kirnbauer, Baker Hughes Incorporated
Intelligent Well System (IWS) completions provide absolute control over reservoir exploitation. The four most important reasons to install an IWS completion are to maximize final recovery of reserves, accelerate/optimize production, reduce intervention operations and minimize environmental impact.
The key factor in maximizing final recovery with an IWS completion is to provide the capability of modifying the production or injection conditions of the well according to the depletion process of the reservoirs or as the result of changing operational conditions. This is active control. The purpose of this control concept is to provide maximum capability to adapt to the variable conditions of the reservoir. There are two control levels: on-off and adjustable (choking capability).
MAXIMIZING FINAL RECOVERY
A coherent reservoir exploitation strategy is required to maximize final recovery of reserves in an economical way. Most of the time, the reservoir operational conditions are very complex, in some cases due to reservoir characteristics (deposition environment, many intercalations, high pressure/high temperature, faults, low or high productivity, gas cap, aquifers, etc.) and in other cases because of specific decisions made during the exploitation cycle. Through the control of the production or injection parameters of the wells, IWS completions help to correct or reduce the uncertainty associated with reservoir exploitation, increasing the possibility of maximizing final recovery of reserves.
ACCELERATE AND OPTIMIZE PRODUCTION
This reservoir exploitation strategy should address reducing exploitation time due to economic, regulatory or strategic reasons. The ideal application for IWS completions is for producing at the same time from different formations with different reservoir characteristics (petrophysical or fluids) or different energy levels (pressure). The variable to be controlled for optimizing flow of fluids is the bottomhole flowing pressure per zone (PWF).
IWS completions can be used for controlling different formations or reservoirs at the same time, maximizing production per zone, and reducing risks associated with cross flow or differential depletion. As a result of this control strategy, production is optimized (optimal production profiles) and the recovery is accelerated. Gauges installed per zone monitor the PWF and let engineering personnel (in charge of making key decisions) interpret specific tendencies for making the right decisions.
REDUCE INTERVENTION COSTS
IWS completions are designed to last for the life of the well. The design for each well is made to afford most of the possible operational situations that could happen in any period of the field life (e.g., water or gas channeling, differential depletion, production or injection profile issues). Obviously, the gauges installed provide real-time data per zone that is used for reducing uncertainties, optimizing production or injection, and making proactive rather than reactive decisions.
Reducing intervention in deepwater wells is important because of the high costs involved. In that sense, many operators would choose higher initial investment if it reduces future operational costs and risks associated with intervention due to problems they did not initially expect. However, if an intervention becomes imperative after the intelligent well system completion is installed (e.g., for correcting a problem associated with productivity), the IWS completion offers the flexibility of diversion.
MINIMIZE ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT
Buildup tests, workovers and running production logs are well interventions. In all these cases, the risk of generating an environmental impact is always there in traditional well completions.
If the IWS completion installed has gauges for monitoring well behavior and for interpreting reservoir exploitation strategy, chemical injection systems for reducing risk associated with plugs, and trained personnel monitoring the data received through signals these systems generate, then the risks of proceeding with well intervention would be very low because of the decisions associated with reservoir exploitation strategies will be proactive (prevention) instead of reactive (corrections).
Figure 1 shows the typical process service company technical personnel follow for selecting the appropriate design during an IWS analysis. The first part of the process (colored) is associated with reservoir and production analysis. The second part of the process (not colored) shown in Fig. 1 is the IWS completion, economics proposal, manufacturing process, quality control, HS&E procedures and field execution.
|
|
|
Fig. 1. Flow diagram for selecting, installing and managing an IWS completion.
|
|
Reservoir and production analyses are performed to determine the IWS completion configuration, control philosophy, control levels, gauge specifications, chemical injection needs, new production behavior and possible new recovery factor; taking into account the information provided by the customer.
Nodal analysis is an important tool for determining initial production condition (total or per zone). Additionally, this analysis helps in configuring the control valve adjustable internal positions (mechanical configuration) and for determining the additional production that would be obtained with this application. However, this information is only one snapshot (the solution in a specific moment during the life of the well).
Currently, service company technical personnel perform near-wellbore analysis using reservoir simulators, with the objective of estimating the future behavior of the well considering the current or new exploitation strategy. In addition to initial production, it is now possible to predict possible scenarios associated with reservoir exploitation, with the objective of designing the IWS completion for most of the operational conditions that would be occur during the exploitation life of the reservoirs.
IWS APPLICATIONS
In general, IWS completions are well suited for these applications: commingled production, correction of production or injection profiles issues, deepwater wells and dump-flood strategies.
COMMINGLED PRODUCTION
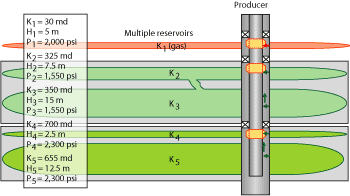
Some fields have two or more reservoirs that could be produced at the same time (usually at different depths). However, these reservoirs could have different petrophysical properties, fluid characteristics and/or different pressures. Using an IWS completion lets the operator simultaneously produce from these reservoirs, reducing risks related to cross flow and differential depletion. An IWS completion accelerates production by taking advantage of real-time monitoring and active control. Figure 2 shows a possible reservoir example for this application.
|
|
|
Fig. 2. Commingled production from three reservoirs.
|
|
INJECTION PROFILE ISSUES
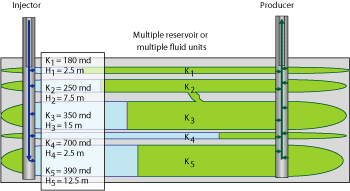
For a number of reasons, many oil and gas reserves have been bypassed during the reservoir exploitation process. One reason is that reservoirs can be subdivided (in many cases) by some fluids units inside the same reservoir with different petrophysical properties. In many cases, no vertical communication between these flow units exists. Additionally, these flow units can have different volumes. Figure 3 shows an example of injection and production profile issues. As a result of this normal characteristic of reservoirs, differential depletion occurs (some flow units deplete faster than others) during the production process or differential replacement occurs (some fluids units build up their pressure faster than others), when injecting fluids for pressure support.
|
|
|
Fig. 3. Reservoir with different flow units and injection profile problems.
|
|
Traditional solutions can be tried to correct or to avoid these issues (e.g., mechanical or chemical blocking, selective completions, density control during perforating), but most of the time these techniques will not provide a permanent solution because reservoir conditions are changing permanently as consequence of exploitation. In this sense, IWS completions (active control) are the best solution for this typical problem. The idea is to produce or inject (through active control valves) the fluids that each flow unit has the capacity for or requires, according to its petrophysical properties or energy levels. Figure 4 shows movement of fluids from injector wells to a producer well in a scenario of no uniform injection (injection profile issues).
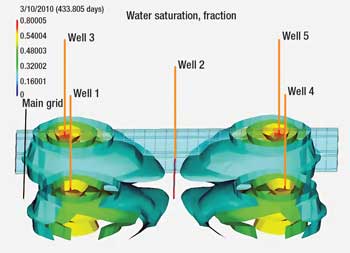
For this example, it can be observed that the fluid injected through flow unit number four (injector well) will arrive faster to the producer well compared with other fluids units. Once this happens, it will be very difficult to recover the reserves associated with the other fluid units (1, 2, 3 and 5).
Figure 4 shows the same behavior as in Fig. 3. However, in this case a reservoir simulator was used to understand better the behavior at the reservoir level. For this analysis, one producer and four injector wells were used (with the same number of fluid units previously discussed).
It can be observed that through Zone 4 (Fig. 3) the water will arrive first from the injector well to the producer well. This means that a good part of the reserves would be bypassed if control actions in injector wells are not taken (this is the kind of problem operators try to avoid daily). Figure 4 confirms the information interpreted in Fig. 3.
|
|
|
Fig. 4. Simulation of channeling process of one specific flow unit. IWS completions can avoid or correct problems like this.
|
|
OFFSHORE AND DEEPWATER WELLS
One of the most complex and challenging applications for IWS completions is offshore, especially deepwater. The obvious aspects of the complexity are high-pressure high-temperature, extreme deep conditions, high levels of uncertainties associated with geological and reservoir aspects, etc. Additional challenges are: high drilling costs, high workover costs, high costs of surface and marine facilities and environmental regulations.
Uncertainty levels associated with exploitation are higher compared to traditional land reservoirs, especially because interventions are not economical. Well completions are designed to accommodate most of the possible contingencies. For this reason, IWS completions are frequently installed in this kind of well. This includes the most sophisticated real-time monitoring systems and control valves with maximum flexibility (choking capability) for making the right decisions at the right time.
One of the most important objectives of offshore/deepwater exploitation strategies is to minimize the number of wells to be drilled, while maximizing final recovery of reserves. For this, well architecture (vertical, highly deviated, horizontal, multilateral, etc.) is fundamental, and for all these cases IWS completions are an ideal solution.
DUMP FLOOD STRATEGIES
Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR) strategies are among the most complex and successful methods for maximizing final recovery of reserves. Surface facilities, operations and logistics associated with EOR operations are very expensive, especially if they are used in offshore or in deepwater projects. Reducing costs in these projects is highly desirable.
In some fields, an aquifer or gas cap with enough energy and reserves (water or gas) could be used for providing fluids with enough energy for injecting directly into some reservoirs or formations. This strategy takes advantage of a natural deposition and migration process that occurred in the past and is now available in the field during exploitation. The idea is to install an IWS completion, proceed to produce a specific fluid with energy (water or gas), and injecting that fluid in a specific volume on each reservoir that requires it for maintaining the replacement factor in the values specified by the exploitation strategy, before that fluid arrives at surface. Obviously, adjustable control valves are the key factor for optimizing the replacement factor and, as consequence, the recovery factor of the field.
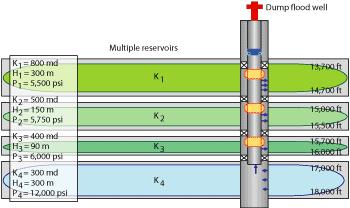
Figure 4 shows an example of a dump flood. The different petrophysical properties and energy values of the reservoirs (different green colors) and of the aquifer (blue color) can be seen. Additionally, Fig. 5 shows the possible mechanical configuration of the IWS completion for this well. In this case, the control valves (yellow color) are adjustable for controlling the water volume to be injected into each reservoir.
|
|
|
Fig. 5. Dump flood example. Aquifer is used for injection into other formations.
|
|
CONTROL PHILOSOPHY
A normal selective completion using sliding sleeves (mechanically activated), with packers between different zones, was once the most sophisticated system for trying to control commingled production. Obviously, these systems required wireline or coiled tubing for activation. The advantages and disadvantages of these mechanical systems are:
Advantages
? Low cost of sliding sleeve
? Low cost of packers
? Can exploit more than one zone simultaneously
Disadvantages
? Choking does not control flow from different zones
? Cross flow cannot be controlled
? Problems in a zone often require shutting off the zone
? Production or injection problems cannot be corrected
? Wireline operations increase the risk of fishing
? Reservoir cannot be monitored in real time
? Possibility of deferred production
? Possibility of environmental impacts
Electrical and hydraulic are the two methods of bottomhole control. Hydraulically actuated systems are the most popular control systems in current use.
HYDRAULIC ACTIVATED SYSTEM, TWO POSITIONS (ON-OFF)
This system requires control lines installed with the completion for activation and feed-thru packers for isolation. The most important advantages and disadvantages are:
Advantages
? Multiple formations can be produced simultaneously
? Multiple formations can be monitored in real time
? Control valves can be activated remotely
? Well test can be performed without intervention
? Does not require maintenance
Disadvantages
? Completion cost is higher than mechanical systems
? Flow from different zones cannot be choked
? Cross flow cannot be controlled
? Problems in a zone often require shutting off the zone
? Production or injection profile problems cannot be corrected
It can be observed that these systems have more advantages than mechanically activated systems, but they have some disadvantages that are crucial from a reservoir strategy point of view. However, some applications would require these specific control philosophy equipments.
HYDRAULIC ACTIVATED SYSTEM, MULTIPLE POSITIONS (CHOKING CAPABILITY)
These systems require control lines installed with the completion for activation and feed-thru packers for isolation. The most important advantages and disadvantages are:
Advantages
? Total control of production or injection profiles
? No cross flow between different zones
? Real-time monitoring of different zones (producing or injecting
? Control valves can be activated remotely
? Well test can be performed without intervention
? Operations associated with production or injection optimization can be performed online (closed loop)
? Does not require maintenance
Disadvantages
? Completion cost is higher than mechanical systems
It is obvious that IWS completions with choke capability have more advantages and fewer disadvantages. They offer the maximum control of most of the possible operational conditions that could happen during the lifecycle of the well.
IWS completions offer flexibility and reliability, but the most important aspect of this technology is its ability to adapt to changing well conditions, whether these changes are part of a planned reservoir exploitation strategy or an unplanned event.
Finally, it is important to note that each IWS completion application is different, and control requirements could vary from one application to other. But in general, IWS completions with choke capability will increase the possibility of higher reserves recovery compared to traditional completions (no control), mechanically activated systems, on-off systems, or any other control technology including passive control completion systems such as inflow control devices.
Detailed analysis, evaluation, and simulation must be performed to determine the correct approach to an IWS completion to get the greatest value from this technology. An IWS completion is the key component of an exploitation strategy to maximize final recovery of reserves through maximum control, real time monitoring and closed loop capability. IWS completions can help operators make the right decision at the right time by reducing uncertainty levels.
楊寶劍 是振威(全球)石油網的高級技術編輯,在石油技術資訊行業有八年的學識和經驗。他源源不斷地提供石油行業全球最新的技術創新��、研發成果����、現場應用情況等信息。如果你對該項新技術有任何的疑問,或者對“新技術新產品”未來的內容有任何問題或建議����,請聯系楊寶劍編輯 +86 10-58236512 Email:allenyo@zhenweiexpo.com 歡迎與行業互動����!